Types of dialysis: steps, costs, and complications
Kidney dialysis is a procedure that is a substitute for many of the normal functions of the kidneys. Dialysis allows patients with kidney failure a chance to live productive lives.There are two types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Each type of dialysis has advantages and disadvantages. Patients can often choose the type of long term dialysis that best matches their needs.
Patients usually require dialysis when the waste products in their body become so high that they start to become sick from them. Doctor measures several blood chemical levels Such as "creatinine level" and the "blood urea nitrogen" (BUN) level to decide when dialysis is necessary.If the patient is experiencing a major inability to rid the body of excess water, or is complaining of problems with the heart, lungs, or stomach, or difficulties with taste or sensation in their legs, dialysis may be indicated even though the creatinine clearance has not fallen to the 10-12 cc/minute level.
What is the role of kidneys and what role does dialysis play?
Dialysis helps the body by performing the functions of failed kidneys. The kidney has many roles. An essential job of the kidney is to regulate the body's fluid balance. It does this by adjusting the amount of urine that is excreted on a daily basis. On hot days, the body sweats more. Thus, less water needs to be excreted through the kidneys. On cold days, the body sweats less. Thus, urine output needs to be greater in order to maintain the proper balance within the body. It is the kidney's job to regulate fluid balance by adjusting urine output.Another major duty of the kidney is to remove the waste products that the body produces throughout the day. As the body functions, cells use energy. The operation of the cells produces waste products that must be removed from the body. When these waste products are not removed adequately, they build up in the body. An elevation of waste products, as measured in the blood, is called "azotemia." When waste products accumulate they, cause a sick feeling throughout the body called "uremia."
types of dialysis
There are two main types of dialysis: "hemodialysis" and "peritoneal dialysis." Hemodialysis uses a special type of filter to remove excess waste products and water from the blood. Peritoneal dialysis uses a fluid that is placed into the patient's abdominal cavity through a special plastic tube to remove excess waste products and fluid from the body.
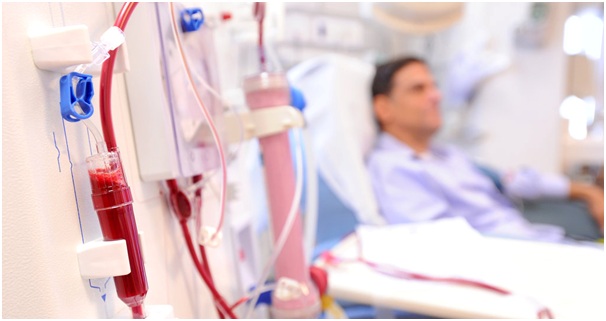
hemodialysis
During hemodialysis, blood passes from the patient's body through a filter in the dialysis machine, called a "dialysis membrane." For this procedure, the patient has a specialized plastic tube placed between an artery and a vein in the arm or leg (called a "gortex graft"). Sometimes, a direct connection is made between an artery and a vein in the arm. This procedure is called a "Cimino fistula." Needles are then placed in the graft or fistula, and blood passes to the dialysis machine, through the filter, and back to the patient. If the patient requires dialysis before a graft or a fistula is placed, a large diameter catheter is placed directly into a large vein in the neck or leg in order to perform dialysis. In the dialysis machine, a solution on the other side of the filter receives the waste products from the patient.
Peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis uses the patients own body tissues inside of the belly (abdominal cavity) to act as the filter. The abdominal cavity is lined with a special membrane, the peritoneal membrane. A plastic tube called a " peritoneal dialysis catheter" is placed through the abdominal wall into the abdominal cavity. A special fluid is then flushed into the abdominal cavity and washes around the intestines. The peritoneal membrane acts as a filter between this fluid and the blood stream. By using different types of solutions, waste products and excess water can be removed from the body through this process.
What does the patient do during dialysis?
Hemodialysis
Treatment for hemodialysis usually takes place in a hemodialysis unit. This is a special building that is equipped with machines that perform the dialysis treatment. Special equipment adds the proper materials to purified water for the dialysis machines. The dialysis unit is also the place where patients can receive dietary counseling and help with social needs.
Patients generally go to the dialysis unit three times a week for treatment. Before treatment, patients weigh themselves so that excess fluid accumulated since the last dialysis session can be measured. Patients then go to assigned chairs that are like lounge chairs. The area of the graft or fistula (the connection between the artery and vein), is cleaned thoroughly. Two needles are then inserted into the graft or fistula. One takes the blood to the machine where it is cleaned. The other needle allows blood that is returning to the patient to go back into the patient's body.
Treatments last from 2 ½ to 4 ½ hours. During this time, the dialysis staff checks the patient's blood pressure frequently and adjusts the dialysis machine to ensure that the proper amount of fluid is being removed from the patients body. Patients can read, watch television, sleep, or do other work during treatment. On occasion, patients who are very motivated may be able to perform dialysis themselves at home in a process called home hemodialysis.
Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis requires the patient to play a more active role in their dialysis treatment. Of primary importance is the patient's responsibility for maintaining a clean surface on the abdomen and catheter, where treatment is administered, in order to prevent infection.
In this process, the patient weighs herself/himself to determine the fluid to be used. The patient then puts on a mask and cleans the peritoneal catheter site. Fluid that has been allowed to stay in the peritoneal cavity is drained back into the plastic bag that originally contained the fluid. The patient then disconnects this bag and connects a new bag of solution that is allowed to drain into the peritoneal cavity. Once the fluid is in the body, the new bag is rolled up and placed in the patient's underwear until the next treatment. This procedure usually takes 30 minutes to accomplish and must be done four to five times a day.As an alternative to this treatment, some patients on peritoneal dialysis use a machine called a "cycler." This cycler is used every night. Five to six bags of dialysis fluid is used on the cycler and the machine automatically changes the fluid while the patient sleeps.
What are the advantages of the different types of dialysis?
Each of the two types of dialysis, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, has advantages and disadvantages. It is up to the patient and doctor to decide which of these procedures is best by considering his life style, other medical conditions, support systems, and how much responsibility and participation in the treatment program he desires.
Regardless of which type of dialysis is chosen, patients have certain responsibilities such as following a diet program, watching their fluid intake and taking special vitamins and other medicines to control blood pressure and calcium and phosphorus balance.For many patients, the major advantage of hemodialysis is minimal participation in the treatment. However, patients are required to adhere to a specific schedule and travel to the dialysis unit three times a week.
Hemodialysis also requires stricter diet control and fluid control than peritoneal dialysis.For those patients preferring more independence, peritoneal dialysis allows for more flexible scheduling and can be performed at home. The patient must undergo a certain amount of dialysis each day, but can alter the exact timing of the dialysis procedure.Kidney disease is a serious condition. In people with chronic kidney failur , the kidneys are unlikely to recover, but dialysis can enhance wellbeing and prolong life for up to 20 years or more.
Does kidney dialysis hurt?
Dialysis treatment itself is painless. Some people have discomfort when being connected to the hemodialysis machine or at the end of a PD drain cycle. If this happens to you, mention it to your healthcare team so they help reduce any minor pain you experience.
Adverse effects of kidney dialysis
People who depend on kidney dialysis may experience:
Muscle cramps
Itchy skin
Low blood pressure, particularly in people with diabetes
Sleep problems, sometimes due to itchiness, restless legs, or small breaks in breathing
Fluid overload
Infections or ballooning at the access site for dialysis
Depression and mood fluctuations
